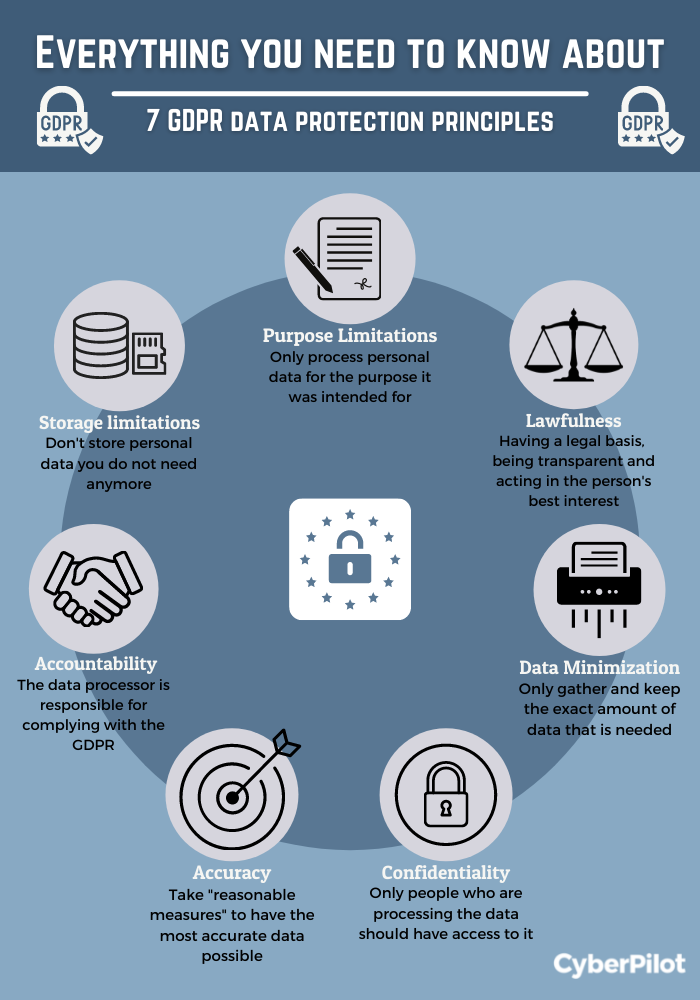
GDPR compliance refers to adhering to the General Data Protection Regulation, a set of rules governing data privacy and protection for individuals within the European Union (EU). The seven principles of GDPR encompass lawful, fair, and transparent processing of personal data; purpose limitation; data minimization; accuracy; storage limitation; integrity and confidentiality; and accountability.
As businesses collect and process personal data, they must ensure compliance with these principles to safeguard individuals’ privacy rights. In today’s digital era, protecting personal data is crucial to maintain trust and transparency in business operations. With GDPR, businesses are mandated to prioritize the privacy and security of individuals’ personal information, fostering a more ethical and responsible data handling culture.
Understanding and implementing the seven GDPR principles is essential for businesses to navigate the regulatory landscape effectively while building a foundation of trust with their customers. By incorporating these principles into their data management practices, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to ethical data handling and ensure compliance with the GDPR, ultimately enhancing their credibility and reputation in the market.
Introduction To Gdpr Compliance
What is GDPR? GDPR, or General Data Protection Regulation, is a set of regulations designed to protect the personal data and privacy of individuals within the European Union (EU) and the European Economic Area (EEA).
Why is GDPR Compliance Important? Compliance with GDPR is crucial for businesses that handle personal data of EU residents. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines and damage to the reputation of the organization.
Principle 1: Lawfulness, Fairness, And Transparency
Gdpr Compliance refers to the General Data Protection Regulation, which sets out the rules for how personal data should be processed and protected. The first principle, Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency, requires that personal data must be processed lawfully, fairly, and in a transparent manner. This means organizations must have a legal basis for processing data, and individuals should be informed about how their data is being used. Key requirements include obtaining consent for data processing, providing privacy notices, and ensuring data processing is done fairly. Examples of compliance include obtaining explicit consent before processing sensitive personal data and providing clear and easily accessible privacy policies.
Principle 2: Purpose Limitation
| Principle 2: Purpose Limitation |
Understanding the Principle: The purpose limitation principle is an essential aspect of GDPR compliance. It emphasizes the importance of clearly defining the purpose for collecting and processing personal data. Organizations should ensure that data is collected for specified and legitimate purposes, and not further processed in a manner that is incompatible with those original purposes. This principle promotes transparency and user control over how their data is used.
Key Requirements: To comply with this principle, organizations must identify and document the lawful basis for data processing, clearly communicate the purposes to individuals, and ensure that data is not used for other undisclosed purposes. They also need to regularly review the relevance and necessity of the data they collect and decide if it aligns with the identified purposes.
Examples of Compliance: A company that collects customer data solely for order fulfillment purposes and does not share it with third parties without the customer’s explicit consent is adhering to the purpose limitation principle. Similarly, an organization that obtains consent from users before using their data for marketing purposes demonstrates compliance with this principle.

Credit: dataprivacymanager.net
Principle 3: Data Minimization
Principle 3 of GDPR emphasizes data minimization, requiring organizations to limit the collection and storage of personal data to what is necessary for specific purposes. This principle helps protect individuals’ privacy by reducing the risk of unauthorized access and potential misuse of their personal information.
|
Understanding the Principle: Data minimization is a crucial aspect of GDPR compliance. It requires organizations to limit the collection of personal data to what is necessary for the intended purpose. Businesses must ensure that they do not gather excessive or irrelevant data, as this could potentially infringe on individuals’ privacy rights. By adopting data minimization practices, companies can demonstrate their commitment to protecting user data and reducing the risks associated with data breaches or unauthorized access. Key Requirements: To comply with the data minimization principle, organizations should actively review and assess the data they collect, ensuring that it is relevant, accurate, and not excessive for the intended purpose. Businesses should also establish retention schedules to determine how long data can be retained before being securely deleted or anonymized. Examples of Compliance: Examples of complying with the data minimization principle include implementing anonymization techniques, conducting regular data audits, and using privacy-enhancing technologies. Companies can also minimize data by using pseudonymization methods or providing individuals with options to control and limit the data they share. |
Principle 4: Accuracy
The fourth principle of GDPR is Accuracy. It requires organizations to ensure that personal data they hold is accurate and up-to-date. Inaccurate data must be rectified or erased without delay. This principle is crucial as it safeguards individuals from potential harm caused by incorrect or outdated information.
Key Requirements:
- Organizations must take reasonable steps to ensure the accuracy of personal data.
- If necessary, personal data should be updated or corrected.
- Inaccurate data must be erased or rectified immediately.
Examples of Compliance:
| Scenario | Compliance |
|---|---|
| A customer notifies a company of a change in their address. | The company promptly updates the customer’s information in their database. |
| An organization discovers inaccurate data during a routine data audit. | The organization corrects the data and updates their records accordingly. |

Credit: www.lexology.com
Principle 5: Storage Limitation
The fifth principle of GDPR is storage limitation, which emphasizes the need to only retain personal data for as long as necessary. Under this principle, organizations should establish clear time constraints for data storage and regularly review and delete data that is no longer required. This principle aims to prevent the indefinite retention of personal data and ensures that organizations are responsible and accountable for managing data throughout its lifecycle.
Understanding The Principle
The principle of storage limitation requires organizations to assess and determine the appropriate retention period for personal data based on its purpose. This means that organizations must establish clear guidelines on how long personal data will be stored and regularly review and revise these timeframes. By implementing proper storage limitation practices, organizations can minimize the risks associated with holding onto unnecessary personal data, such as data breaches or unauthorized use.
Key Requirements
- Define and document data retention policies and procedures
- Regularly review and update data storage timeframes
- Implement mechanisms to ensure safe and secure deletion of data
- Ensure compliance with applicable legal and regulatory requirements
Examples Of Compliance
| Industries | Compliance Measures |
|---|---|
| Financial Services | Implementing data retention schedules and securely disposing of data once it reaches its expiration date |
| E-commerce | Regularly reviewing and purging customer data that is no longer needed for business transactions or legal purposes |
| Healthcare | Establishing retention periods for medical records and securely disposing of records once the retention period has ended |
Credit: www.progress.com
Frequently Asked Questions On What Is Gdpr Compliance 7 Principles Of Gdpr Explained
What Is Gdpr Compliance?
GDPR compliance refers to following the rules and regulations set forth by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). It ensures that businesses handle personal data of EU citizens responsibly, protect their privacy, and obtain proper consent for data collection and processing.
Why Is Gdpr Important?
GDPR is important because it gives individuals more control over their personal data and enhances their privacy rights. It also promotes transparency and trust between businesses and consumers, encourages better data handling practices, and imposes significant penalties for non-compliance.
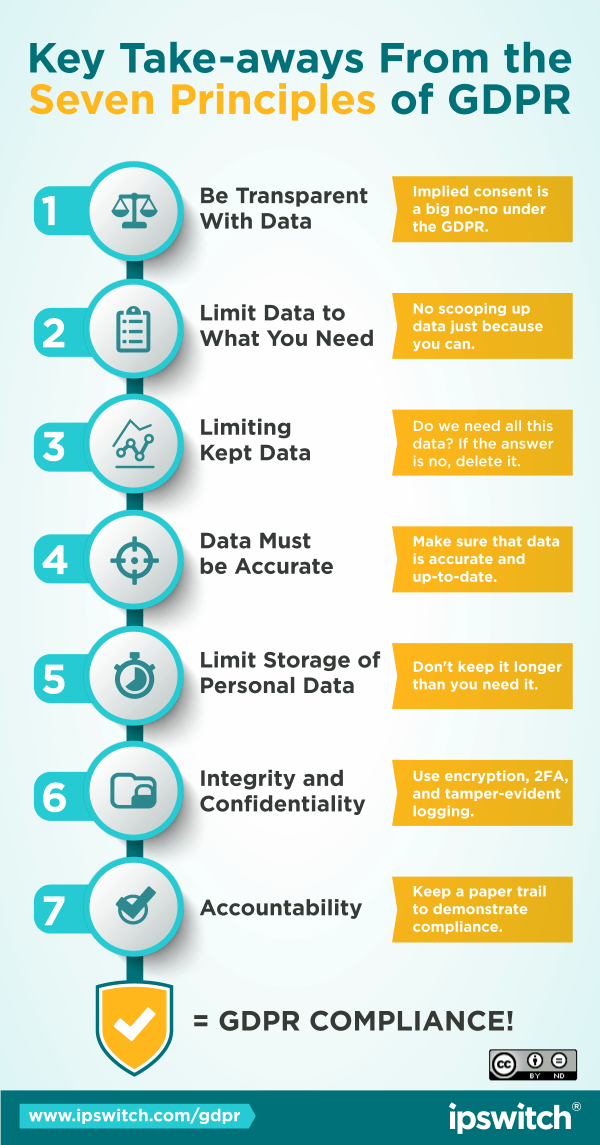
What Are The 7 Principles Of Gdpr?
The 7 principles of GDPR are:
1. Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency: Data processing must be legal, transparent, and fair to individuals. 2. Purpose limitation: Data should be collected for specific and legitimate purposes and not be processed in a way incompatible with those purposes. 3. Data minimization: Only collect and retain the personal data that is necessary for the intended purpose. 4. Accuracy: Keep personal data accurate and up-to-date. 5. Storage limitation: Personal data should not be kept longer than necessary. 6. Integrity and confidentiality: Implement appropriate security measures to safeguard personal data. 7. Accountability: Organizations are responsible for complying with GDPR and demonstrating their compliance.
Conclusion
To conclude, understanding GDPR compliance and its seven principles is crucial for businesses today. By prioritizing data protection, accountability, and transparency, organizations can build trust with their customers, avoid hefty fines, and uphold the privacy rights of individuals. Compliance may require adjustments and investments, but the long-term benefits far outweigh the initial efforts.
Embracing GDPR not only ensures legal compliance but also demonstrates a commitment to ethical business practices in the digital age. Stay informed, adapt your processes, and prioritize data protection to navigate the changing landscape successfully.